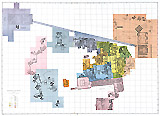
Central Field (Hassan): Site: Giza; View: G 8130, G 8124
-
- Tomb Owner
- Niankhre (G 8130)
-
- Excavator
- Selim Hassan (Bey), Egyptian, 1886–1961
-
- Abou-Ghazi No (ASAE 58 [1964])
- 71
-
- Hassan No.
- Ny-'ankh-Ra'
- Niankhre
-
- PorterMoss Date
- Probably Dynasty 5
-
- Site Type
- Rock-cut tomb
-
- Shafts
- burial chamber; chapel; courtyard
-
- Remarks
- Mastaba built northeast of G 8124 (Rock Cut Tomb (F-11)) which is north of G 8090 (Lepsius 90) and south of G 8140 (Niuserre). Excavated in 1932-1933 by Hassan.
-
- EMC_TR_11.5.46.3
-
- EMC_TR_11.5.46.4
-
- EMC_TR_11.5.46.5
-
- GEM_7463
-
- EMC_JE_88187
-
Head of basalt statue of a man
- GEM_14205
-
- EMC_TR_11.5.43.6
-
- EMC_TR_11.5.43.7
-
- EMC_TR_11.5.43.8
-
Eaton-Krauss, Marianne. "Pseudo-Groups." In Rainer Stadelmann and Hourig Sourouzian, eds. Kunst des Alten Reiches: Symposium im Deutschen Archäologischen Institut Kairo am 29. und 30. Oktober 1991. Sonderschrift des Deutschen Archäologischen Institut Abteilung Kairo 28, Mainz am Rhein: Verlag Philipp von Zabern, 1995, p. 70, #14.
Hassan, Selim. Excavations at Gîza 4: 1932-1933. Cairo: Government Press, 1943, pp. 151-158, figs. 106-112, pls. 41-46.
Hassan, Selim. Excavations at Gîza 9: 1936-37-38. The Mastabas of the Eighth Season and their Description. Cairo: General Organisation for Government Printing Offices, 1960, folded plan, F/G-11.
Porter, Bertha, and Rosalind L.B. Moss. Topographical Bibliography of Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphic Texts, Reliefs, and Paintings 3: Memphis (Abû Rawâsh to Dahshûr). Oxford: The Clarendon Press, 1931. 2nd edition. 3: Memphis, Part 1 (Abû Rawâsh to Abûsîr), revised and augmented by Jaromír Málek. Oxford: The Clarendon Press, 1974, pp. 234-235, plan 21, D-1/2.
Reisner, George A. A History of the Giza Necropolis 1. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1942, p. 243 [bottom, 1], fig. 150.
Ancient People
-
- Type Tomb Owner
- Remarks Owner of G 8130. Entrance architrave and drum inscribed for Niankhre, identified as [sA nswt smr watj Hrj-sStA n pr-dwAt Hrj-sStA nswt m swt=f nbt jmj-jb n nb=f mrr nb=f Xrj-Hb Hrj-sStA n mdw-nTr jmj-r kAt nbt nt nswt Xrj-tp nswt smsw js jwn-knmwt mdw rxjjt xrp wsxt wD wDa-mdw mAa n Hrjw-wDbw] king's son, sole companion, secretary of the House of Morning, secretary of the king in all his places, he who is in the heart of his lord, beloved of his lord, lector-priest, secretary of the sacred writings, overseer of all royal works, royal chamberlain, elder of the is-chamber, iun-kenmut priest, staff of the commoners, director of the broad hall, true giver of judgements to the masters of reversion-offerings; in situ in G 8130.
Modern People
-
- Type Excavator
- Nationality & Dates Egyptian, 1886–1961
- Remarks Egyptologist; Sub Director General. Nationality and life dates from Who was Who in Egyptology. (1886-1961) Egyptian Egyptologist; born Mit-Nagi, 15 April 1886, he studied at the Higher Teacher's College, Cairo under Kamal (q.v.); in 1912 he became a teacher and in 1921 obtained a post in the Egyptian Museum as assistant keeper; he studied in Paris 1923-7 at the Ecole Pratique des Hautes Etudes; he was the first Egyptian to be appointed as a Professor of Egyptology in the Universitv of Cairo, 1928 - 36; he was later made Deputy Director of the Egyptian Antiquities Service responsible for the care of all monuments in the Nile valley, 1936-39; Ph.D. Vienna University, 1935; stimulated by the archaeological work of P. E. Newberry (q.v.) and Junker (q.v.)he began an active career in excavations with the clearance of some of the Giza mastabas in 1929; the excavations carried on by him in this necropolis continued until 1939 by which time a great deal of digging had been achieved, published in 10 parts; he also cleared the Sphinx and its temple, for the first time completely digging out the great amphitheatre around it and ensuring that it would not be buried by send again so easily; he wrote a study on this work and on the temple of Amenhotep II here; in addition the so-called Fourth Pyramid or the palace-façade tomb of Queen Khent-kawes of the Fourth Dynasty was investigated and also the funerary town of the priests associated with it; he later worked on the Unas causeway at Saqqara and at the valley temple of this king, discovering some of the mastabas in this area and two great subterranean tombs dated to the Second Dynasty; his final excavations at Giza were carried out on the east and south faces of the Great Pyramid and at the mortuary temple of King Khufu, 1938-9; he also took part in the campaign to save the monments of Nubia, and wrote a report on this subject; he published about 53 books and articles on Egyptological subjects in English, French, and Arabic, Hymnes religieux du Moyen Empire, 1928; Le Poème dit de Pentaour et Le rapport officiel sur la bataiILe de Qadesh , 1929; Excavations at Giza, 10 pts., 1929-60; The Sphinx. Its History in the Light of recent Excavations, 1949; Report on the Monunents of Nubia,1955Excavations at Saqqara 1937-8, 3 vols., 1975; in Arabic Literature of Ancient Egpt, 2 vols.; Ancient Egypt from Prehistoric Times to the Age of Rameses 11, 6 vols.; he died in Giza, 30 Sept. 1961. AfO 20 (1963), 310 (H. Brunner); Archaeology 14, no, 4 (1961, 293; ASAE 58 (1964), 61- 84 (bibl.) (Dia Abou-Ghazi); Orientalia 31 (1962), 271; Goettinger Miszellen 76 (1984), 78-80; Reid, JAOS 105 (1985), 237, 241-44.
Name of this image
Description of the image duis mollis, est non commodo luctus, nisi erat porttitor ligula, eget lacinia odio sem nec elit. Sed posuere consectetur est at lobortis. Donec sed odio dui.

- Heather ONeill heather@pixelsforhumans.com
- Nicholas Picardo npicardo@fas.harvard.edu
- Luke Hollis luke@archimedes.digital
Hi ! (not you? Login to your account.)
- Cole Test Collection - Tomb Chapels and Shafts
- GPH Test Collection 1
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- ZAP
- ZAP
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Ankhmare
- ZAP
- ZAP
- ZAP
- Hello World
- http://www.pypi.org/
- Hello World
- //pypi.org
- Hello World
- Hello World
- 1'2"3
- a'b"c'd"
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- /..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//../etc/passwd
- Hello World
- Hello World
- ../../../../../../../../../../../../../../../etc/passwd
- Hello World
- file:///etc/passwd
- /etc/passwd
- /..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//../boot.ini
- ../../../../../../../../../../../../../../../boot.ini
- Hello World
- C:\boot.ini
- file:///C:/boot.ini
- file:///C:/win.ini
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- &&/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- &&type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- |/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- |type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- ;/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- ;type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World
- `/bin/cat /etc/passwd`
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello Worldtype %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World&&type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World&&/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- run type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World|/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World|type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World;/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello Worldrun type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World`/bin/cat /etc/passwd`
- Hello World type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World;type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Mr.
- Hello World
- Hello World
- a'b"c'd"
- 1'2"3
- Hello World
- http://www.pypi.org/
- Hello World
- //pypi.org
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- ../../../../../../../../../../../../../../../etc/passwd
- /..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//../etc/passwd
- /etc/passwd
- /..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//../boot.ini
- ../../../../../../../../../../../../../../../boot.ini
- file:///etc/passwd
- C:\boot.ini
- file:///C:/win.ini
- %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- file:///C:/boot.ini
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World
- &&/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- &&type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- |type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- |/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- ;type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- ;/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- `/bin/cat /etc/passwd`
- run type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello Worldtype %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World&&/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World&&type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World|/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World|type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World;/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World;type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World`/bin/cat /etc/passwd`
- Hello Worldrun type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World`/bin/cat /etc/passwd`
- Hello Worldrun type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World
- 1'2"3
- Hello World
- a'b"c'd"
- Hello World
- Hello World
- //pypi.org
- http://www.pypi.org/
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- /..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//../etc/passwd
- ../../../../../../../../../../../../../../../etc/passwd
- /etc/passwd
- ../../../../../../../../../../../../../../../boot.ini
- /..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//../boot.ini
- file:///etc/passwd
- C:\boot.ini
- %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- file:///C:/boot.ini
- file:///C:/win.ini
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- &&/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- ;/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- &&type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- |type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- ;type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- |/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World
- `/bin/cat /etc/passwd`
- Hello World
- Hello World
- run type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World|/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World
- Hello World&&type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World|type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello Worldtype %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World&&/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World;/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World;type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World`/bin/cat /etc/passwd`
- Hello Worldrun type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World
- 1'2"3
- Hello World
- a'b"c'd"
- http://www.pypi.org/
- Hello World
- //pypi.org
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- /..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//../etc/passwd
- ../../../../../../../../../../../../../../../etc/passwd
- /etc/passwd
- file:///etc/passwd
- /..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//..//../boot.ini
- ../../../../../../../../../../../../../../../boot.ini
- %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- C:\boot.ini
- file:///C:/boot.ini
- Hello World
- file:///C:/win.ini
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- &&/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World
- Hello World
- /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World
- &&type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- |/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- |type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- ;/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- ;type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World
- type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World
- /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- `/bin/cat /etc/passwd`
- type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- run type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World
- Hello World/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World
- Hello Worldtype %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World;type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World;/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World&&type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World|/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World&&/bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World
- Hello World type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World|type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello World`/bin/cat /etc/passwd`
- Hello World /bin/cat /etc/passwd
- Hello World type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello Worldrun type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Hello Worldrun type %SYSTEMROOT%\win.ini
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- )
- HttP://bxss.me/t/xss.html?%00
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- !(()&&!|*|*|
- bxss.me/t/xss.html?%00
- Mr.
- Mr.
- ^(#$!@#$)(()))******
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- ;assert(base64_decode('cHJpbnQobWQ1KDMxMzM3KSk7'));
- )))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))))
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- ';print(md5(31337));$a='
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.<esi:include src="http://bxss.me/rpb.png"/>
- ";print(md5(31337));$a="
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- ${@print(md5(31337))}
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- ${@print(md5(31337))}\
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- '.print(md5(31337)).'
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- 1yrphmgdpgulaszriylqiipemefmacafkxycjaxjs%00.
- Mr.
- response.write(9359478*9159837)
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Http://bxss.me/t/fit.txt
- Mr.
- Mr.
- '+response.write(9359478*9159837)+'
- Mr.
- http://bxss.me/t/fit.txt%3F.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- "+response.write(9359478*9159837)+"
- Mr.
- /etc/shells
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- ../../../../../../../../../../../../../../etc/shells
- Mr.
- Mr.
- c:/windows/win.ini
- Mr.
- Mr.
- bxss.me
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- '"()
- Mr.'&&sleep(27*1000)*slthro&&'
- Mr."&&sleep(27*1000)*dkdlrh&&"
- Mr.'||sleep(27*1000)*pfyeyf||'
- Mr."||sleep(27*1000)*vrrigp||"
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.HpwZ3hXw
- Mr.
- Mr.
- Mr.
- -1 OR 2+803-803-1=0+0+0+1 --
- Mr.
- -1 OR 2+253-253-1=0+0+0+1
- Mr.
- -1' OR 2+807-807-1=0+0+0+1 --
- Mr.
- -1' OR 2+110-110-1=0+0+0+1 or 'mIlFOcgT'='
- Mr.
- -1" OR 2+293-293-1=0+0+0+1 --
- Mr.
- if(now()=sysdate(),sleep(15),0)
- Mr.
- Mr.0'XOR(if(now()=sysdate(),sleep(15),0))XOR'Z
- Mr.
- Mr.0"XOR(if(now()=sysdate(),sleep(15),0))XOR"Z
- Mr.
- Mr.-1 waitfor delay '0:0:15' --
- Mr.2H1Mv5Ef'; waitfor delay '0:0:15' --
- Mr.TYNbmTdK' OR 776=(SELECT 776 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))--
- Mr.
- Mr.80a8vca7') OR 501=(SELECT 501 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))--
- Mr.2DjcVzD1')) OR 104=(SELECT 104 FROM PG_SLEEP(15))--
- ../../../../../../../../../../../../../../etc/passwd
- Mr.'||DBMS_PIPE.RECEIVE_MESSAGE(CHR(98)||CHR(98)||CHR(98),15)||'
- ../../../../../../../../../../../../../../windows/win.ini
- Mr.
- file:///etc/passwd
- Mr.'"
- Mr.
- Mr.����%2527%2522\'\"
- ../Mr.
- @@kojE8
- Mr.
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana
- katana